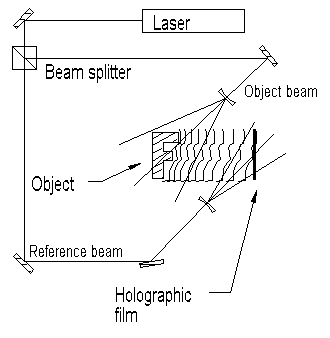

Recording an off-axis hologram. Coherent light from a laser is split into two beams of approximately equal path length. One, the reference beam, falls directly on to the recording medium. The other beam, which may be further split into many beams, illuminates the object. The hologram records the interference pattern between the light reflected, scattered, or diffracted from the object and the reference beam.