Drug rescue of frataxin-dependent neural and cardiac pathophysiology in FA
This project aims to identify the most potent and effective known drugs to investigate treatment of the inherited disease, Friedreich ataxia, motivating pharma to fund more clinical trials.
This international collaborative project between the Cortopassi, Giunti and Pook laboratories aims to test a number of differently-acting drug compounds to identify the most potent and effective known drugs to address Friedreich ataxia.
The drugs we plan to test have all passed through clinical testing in humans (with the exception of RPG109), including the frataxin unsilencers: DMF, Methylene Blue, 109; the mitobiogenesis enhancers: beta-methasone, -epicatechin, resveratrol; and the iron-sulfur cluster stimulator hemin. The drug compounds will initially be tested individually or as mixtures in Friedreich ataxia patient, cells to then identify which compounds effectively rescue deficits of mitochondrial function in cells and tissues of Friedreich ataxia animal models.
We thereby aim to identify the most effective molecules for the physiological rescue of function.
The aim for impact is that our data would motivate pharma to fund more clinical trials to investigate the treatment of Friedreich ataxia.
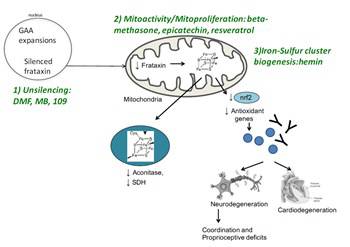 The most effective molecules for the physiological rescue of function
The most effective molecules for the physiological rescue of function
Meet the Principal Investigator(s) for the project
Related Research Group(s)
Genome Engineering and Maintenance - Diverse research network focused on molecular, cellular, organismal and computational aspects of genome biology.
Partnering with confidence
Organisations interested in our research can partner with us with confidence backed by an external and independent benchmark: The Knowledge Exchange Framework. Read more.
Project last modified 12/01/2024